偏最小二乘回归是一种回归形式 。
当使用pls时,新的线性组合有助于解释模型中的自变量和因变量。
在本文中,我们将使用pls预测“收入”。
library(Ecdat)## 'data.frame': 753 obs. of 18 variables:
## $ work : Factor w/ 2 levels "yes","no": 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 ...
## $ hoursw : int 1610 1656 1980 456 1568 2032 1440 1020 1458 1600 ...
## $ child6 : int 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 ...
## $ child618 : int 0 2 3 3 2 0 2 0 2 2 ...
## $ agew : int 32 30 35 34 31 54 37 54 48 39 ...
## $ educw : int 12 12 12 12 14 12 16 12 12 12 ...
## $ hearnw : num 3.35 1.39 4.55 1.1 4.59 ...
## $ wagew : num 2.65 2.65 4.04 3.25 3.6 4.7 5.95 9.98 0 4.15 ...
## $ hoursh : int 2708 2310 3072 1920 2000 1040 2670 4120 1995 2100 ...
## $ ageh : int 34 30 40 53 32 57 37 53 52 43 ...
## $ educh : int 12 9 12 10 12 11 12 8 4 12 ...
## $ wageh : num 4.03 8.44 3.58 3.54 10 ...
## $ income : int 16310 21800 21040 7300 27300 19495 21152 18900 20405 20425 ...
## $ educwm : int 12 7 12 7 12 14 14 3 7 7 ...
## $ educwf : int 7 7 7 7 14 7 7 3 7 7 ...
## $ unemprate : num 5 11 5 5 9.5 7.5 5 5 3 5 ...
## $ city : Factor w/ 2 levels "no","yes": 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1 ...
## $ experience: int 14 5 15 6 7 33 11 35 24 21 ...首先,我们将数据分为训练和测试集来准备数据。
set.seed(777)
train<-sample(c(T,F),nrow(Mroz),rep=T) #50/50 训练/测试拆分在上面的代码中,我们设置“ set.seed函数”以确保可重复性。然后,我们创建了“ train”对象 。
现在,我们使用 “plsr”函数创建模型,然后使用“ summary”函数检查结果。我们 使用交叉验证。下面是代码。
## Data: X dimension: 392 17
## Y dimension: 392 1
## Fit method: kernelpls
## Number of components considered: 17
##
## VALIDATION: RMSEP
## Cross-validated using 10 random segments.
## (Intercept) 1 comps 2 comps 3 comps 4 comps 5 comps 6 comps
## CV 11218 8121 6701 6127 5952 5886 5857
## adjCV 11218 8114 6683 6108 5941 5872 5842
## 7 comps 8 comps 9 comps 10 comps 11 comps 12 comps 13 comps
## CV 5853 5849 5854 5853 5853 5852 5852
## adjCV 5837 5833 5837 5836 5836 5835 5835
## 14 comps 15 comps 16 comps 17 comps
## CV 5852 5852 5852 5852
## adjCV 5835 5835 5835 5835
##
## TRAINING: % variance explained
## 1 comps 2 comps 3 comps 4 comps 5 comps 6 comps 7 comps
## X 17.04 26.64 37.18 49.16 59.63 64.63 69.13
## income 49.26 66.63 72.75 74.16 74.87 75.25 75.44
## 8 comps 9 comps 10 comps 11 comps 12 comps 13 comps 14 comps
## X 72.82 76.06 78.59 81.79 85.52 89.55 92.14
## income 75.49 75.51 75.51 75.52 75.52 75.52 75.52
## 15 comps 16 comps 17 comps
## X 94.88 97.62 100.00
## income 75.52 75.52 75.52输出包括“验证”部分中均方根误差 。因为有17个独立变量,所以有17个成分。 可以看到,在成分3或4之后,因变量中解释的方差几乎没有改善。下面是这些结果图的代码。
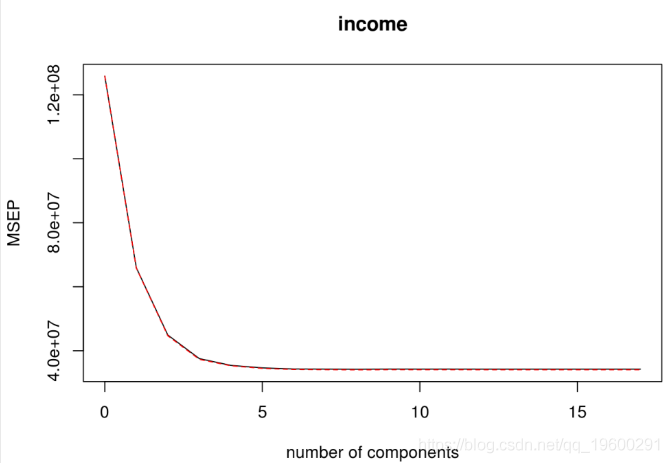
我们将使用我们的模型进行预测。
此后,我们计算均方误差。这是通过从测试集的因变量中减去我们的预测模型的结果来完成的。然后,我们对这些信息求平方并计算平均值。
mean((pls.pred-Mroz$income\[test\])^2)## \[1\] 63386682我们使用传统的最小二乘回归模型运行数据并比较结果。
随时关注您喜欢的主题
## \[1\] 59432814最小二乘模型比偏最小二乘模型好一点,但是如果看一下模型,我们会看到几个不重要的变量。我们删除这些,看看结果如何
summary(lm.fit)##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -20131 -2923 -1065 1670 36246
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) -1.946e+04 3.224e+03 -6.036 3.81e-09 ***
## workno -4.823e+03 1.037e+03 -4.651 4.59e-06 ***
## hoursw 4.255e+00 5.517e-01 7.712 1.14e-13 ***
## child6 -6.313e+02 6.694e+02 -0.943 0.346258
## child618 4.847e+02 2.362e+02 2.052 0.040841 *
## agew 2.782e+02 8.124e+01 3.424 0.000686 ***
## educw 1.268e+02 1.889e+02 0.671 0.502513
## hearnw 6.401e+02 1.420e+02 4.507 8.79e-06 ***
## wagew 1.945e+02 1.818e+02 1.070 0.285187
## hoursh 6.030e+00 5.342e-01 11.288 < 2e-16 ***
## ageh -9.433e+01 7.720e+01 -1.222 0.222488
## educh 1.784e+02 1.369e+02 1.303 0.193437
## wageh 2.202e+03 8.714e+01 25.264 < 2e-16 ***
## educwm -4.394e+01 1.128e+02 -0.390 0.697024
## educwf 1.392e+02 1.053e+02 1.322 0.186873
## unemprate -1.657e+02 9.780e+01 -1.694 0.091055 .
## cityyes -3.475e+02 6.686e+02 -0.520 0.603496
## experience -1.229e+02 4.490e+01 -2.737 0.006488 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 5668 on 374 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.7552, Adjusted R-squared: 0.744
## F-statistic: 67.85 on 17 and 374 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16lm.pred<-predict(lm.fit,Mroz\[test,\])
mean((lm.pred-Mroz$income\[test\])^2)## \[1\] 57839715误差降低很多,这表明最小二乘回归模型优于偏最小二乘模型。此外, 偏最小二乘模型很难解释。因此,最小二乘模型是最受欢迎的模型。
可下载资源
关于作者
Kaizong Ye是拓端研究室(TRL)的研究员。在此对他对本文所作的贡献表示诚挚感谢,他在上海财经大学完成了统计学专业的硕士学位,专注人工智能领域。擅长Python.Matlab仿真、视觉处理、神经网络、数据分析。
本文借鉴了作者最近为《R语言数据分析挖掘必知必会 》课堂做的准备。
非常感谢您阅读本文,如需帮助请联系我们!

 Python梯度提升树、XGBoost、LASSO回归、决策树、SVM、随机森林预测中国A股上市公司数据研发操纵融合CEO特质与公司特征及SHAP可解释性研究|附代码数据
Python梯度提升树、XGBoost、LASSO回归、决策树、SVM、随机森林预测中国A股上市公司数据研发操纵融合CEO特质与公司特征及SHAP可解释性研究|附代码数据 视频讲解|Stata和R语言自助法Bootstrap结合GARCH对sp500收益率数据分析
视频讲解|Stata和R语言自助法Bootstrap结合GARCH对sp500收益率数据分析 Python谷歌商店Google Play APP评分预测:LASSO、多元线性回归、岭回归模型对比研究
Python谷歌商店Google Play APP评分预测:LASSO、多元线性回归、岭回归模型对比研究



