
Logistic回归可以使用glm (广义线性模型)函数在R中执行 。
怎么做测试?
该函数使用链接函数来确定要使用哪种模型,例如逻辑模型,概率模型或泊松模型。
可下载资源
假设条件
广义线性模型的假设少于大多数常见的参数检验。观测值仍然需要独立,并且需要指定正确的链接函数。因此,例如应该了解何时使用泊松回归以及何时使用逻辑回归。但是,不需要数据或残差的正态分布。
并非所有比例或计数都适用于逻辑回归分析
一个不采用逻辑回归的例子中,饮食研究中人们减肥的体重无法用初始体重的比例来解释作为“成功”和“失败”的计数。在这里,只要满足模型假设,就可以使用常用的参数方法。
过度分散
使用广义线性模型时要注意的一个潜在问题是过度分散。当模型的残余偏差相对于残余自由度较高时,就会发生这种情况。这基本上表明该模型不能很好地拟合数据。
但是据我了解,从技术上讲,过度分散对于简单的逻辑回归而言不是问题,即具有二项式因果关系和单个连续自变量的问题。
伪R平方
对于广义线性模型(glm),R不产生r平方值。pscl 包中的 pR2 可以产生伪R平方值。
测试p值
检验逻辑对数或泊松回归的p值使用卡方检验。方差分析 来测试每一个系数的显着性。似然比检验也可以用来检验整体模型的重要性。
Logistic回归示例
Data = read.table(textConnection(Input),header=TRUE)
Data$Total = Data$mpi90 + Data$mpi100
Data$Percent = Data$mpi100 / + Data$Total
模型拟合
Trials = cbind(Data$mpi100, Data$mpi90) # Sucesses, Failures
model = glm(Trials ~ Latitude,
data = Data,
family = binomial(link="logit"))
系数和指数系数
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) -7.64686 0.92487 -8.268 <2e-16 ***
Latitude 0.17864 0.02104 8.490 <2e-16 ***
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) -9.5003746 -5.8702453
Latitude 0.1382141 0.2208032
# exponentiated coefficients
(Intercept) Latitude
0.0004775391 1.1955899446
# 95% CI for exponentiated coefficients
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) 7.482379e-05 0.002822181
Latitude 1.148221e+00 1.247077992
方差分析
Analysis of Deviance Table (Type II tests)
Response: Trials
Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
Latitude 1 72.076 < 2.2e-16 ***
伪R平方
$Models
Model: "glm, Trials ~ Latitude, binomial(link = \"logit\"), Data"
Null: "glm, Trials ~ 1, binomial(link = \"logit\"), Data"
$Pseudo.R.squared.for.model.vs.null
Pseudo.R.squared
McFadden 0.425248
Cox and Snell (ML) 0.999970
Nagelkerke (Cragg and Uhler) 0.999970
模型的整体p值
Analysis of Deviance Table
Model 1: Trials ~ Latitude
Model 2: Trials ~ 1
Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
1 6 70.333
2 7 153.633 -1 -83.301 < 2.2e-16 ***
Likelihood ratio test
Model 1: Trials ~ Latitude
Model 2: Trials ~ 1
#Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
1 2 -56.293
2 1 -97.944 -1 83.301 < 2.2e-16 ***
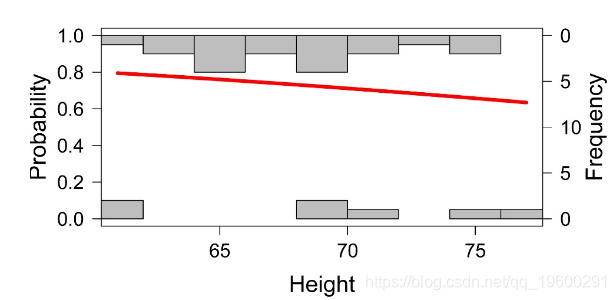
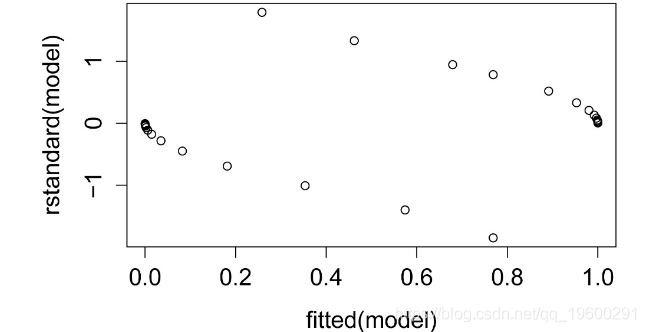
标准化残差图
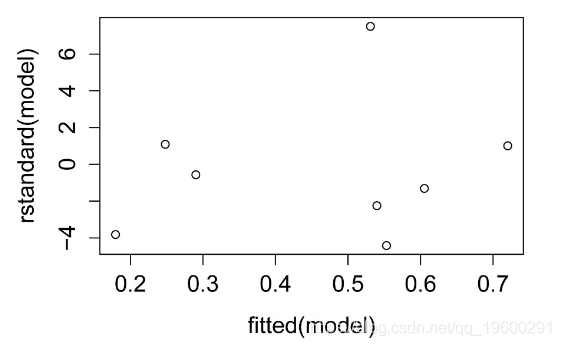

标准化残差与预测值的关系图。残差应无偏且均等。
绘制模型
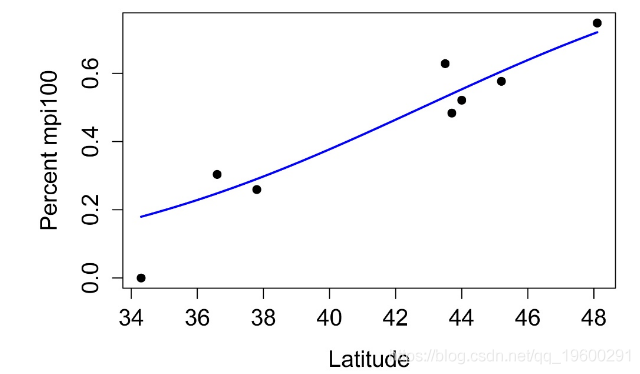

Logistic回归示例
Data = read.table(textConnection(Input),header=TRUE)

模型拟合
model 
系数和指数系数
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) 4.41379 6.66190 0.663 0.508
Height -0.05016 0.09577 -0.524 0.600
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) -8.4723648 18.4667731
Height -0.2498133 0.1374819
# exponentiated coefficients
(Intercept) Height
82.5821122 0.9510757
# 95% CI for exponentiated coefficients
2.5 % 97.5 %
(Intercept) 0.0002091697 1.047171e+08
Height 0.7789461738 1.147381e+0

方差分析
Analysis of Deviance Table (Type II tests)
Response: Insect
Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
Height 1 0.2743 0.6004
Residuals 23
伪R平方
$Pseudo.R.squared.for.model.vs.null
Pseudo.R.squared
McFadden 0.00936978
Cox and Snell (ML) 0.01105020
Nagelkerke (Cragg and Uhler) 0.01591030
模型的整体p值
Analysis of Deviance Table
Model 1: Insect ~ Height
Model 2: Insect ~ 1
Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
1 23 29.370
2 24 29.648 -1 -0.27779 0.5982
Likelihood ratio test
Model 1: Insect ~ Height
Model 2: Insect ~ 1
#Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
1 2 -14.685
2 1 -14.824 -1 0.2778 0.5982
标准化残差图
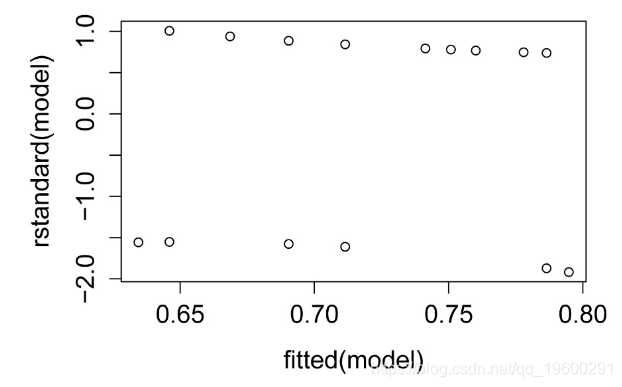

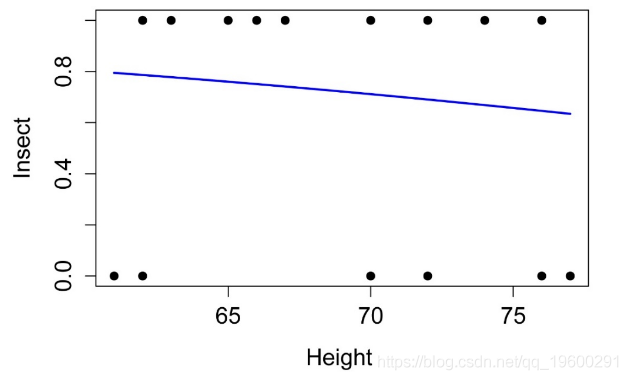
绘制模型
Height Insect Insect.num
1 62 beetle 0
2 66 other 1
3 61 beetle 0
23 72 other 1
24 70 beetle 0
25 74 other 1


Height Insect Insect.num Insect.log
1 62 beetle 0 FALSE
2 66 other 1 TRUE
3 61 beetle 0 FALSE
23 72 other 1 TRUE
24 70 beetle 0 FALSE
25 74 other 1 TRUE


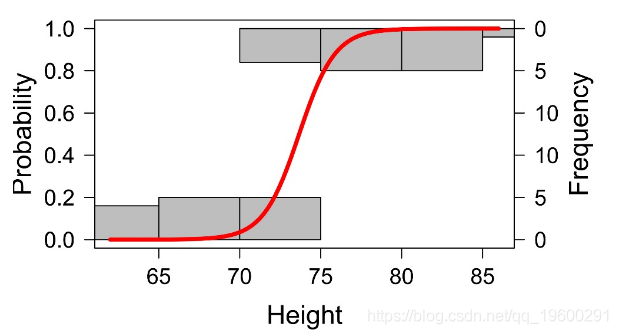
Logistic回归示例
Data = read.table(textConnection(Input),header=TRUE)
model
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
(Intercept) -66.4981 32.3787 -2.054 0.0400 *
Continuous 0.9027 0.4389 2.056 0.0397 *
Analysis of Deviance Table (Type II tests)
Response: Factor
Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
Continuous 1 4.229 0.03974 *
Residuals 27
Pseudo.R.squared
McFadden 0.697579
Cox and Snell (ML) 0.619482
Nagelkerke (Cragg and Uhler) 0.826303
Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
1 27 12.148
2 28 40.168 -1 -28.02 1.2e-07 ***


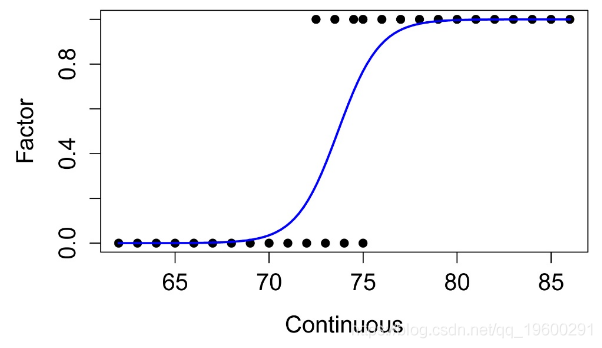
将因子转换为数字变量,级别为0和1
Continuous Factor Factor.num
1 62 A 0
2 63 A 0
3 64 A 0
27 84 B 1
28 85 B 1
29 86 B 1


将Factor转换为逻辑变量,级别为TRUE和FALSE
Continuous Factor Factor.num Factor.log
1 62 A 0 FALSE
2 63 A 0 FALSE
3 64 A 0 FALSE
27 84 B 1 TRUE
28 85 B 1 TRUE
29 86 B 1 TRUE

可下载资源
关于作者
Kaizong Ye是拓端研究室(TRL)的研究员。在此对他对本文所作的贡献表示诚挚感谢,他在上海财经大学完成了统计学专业的硕士学位,专注人工智能领域。擅长Python.Matlab仿真、视觉处理、神经网络、数据分析。
本文借鉴了作者最近为《R语言数据分析挖掘必知必会 》课堂做的准备。
非常感谢您阅读本文,如需帮助请联系我们!

 R语言广义加性模型GAM、Tweedie分布的SaaS客户生命周期价值CLV预测研究——非线性关系捕捉与异方差性适配创新|附代码数据
R语言广义加性模型GAM、Tweedie分布的SaaS客户生命周期价值CLV预测研究——非线性关系捕捉与异方差性适配创新|附代码数据 R语言优化沪深股票投资组合:粒子群优化算法PSO、重要性采样、均值-方差模型、梯度下降法|附代码数据
R语言优化沪深股票投资组合:粒子群优化算法PSO、重要性采样、均值-方差模型、梯度下降法|附代码数据 MATLAB奥运会奖牌预测研究 —CNN神经网络、逻辑回归、Liang-Kleeman信息流、多元回归及随机森林模型的因果关联与概率预测|附代码数据
MATLAB奥运会奖牌预测研究 —CNN神经网络、逻辑回归、Liang-Kleeman信息流、多元回归及随机森林模型的因果关联与概率预测|附代码数据 【视频讲解】R语言海七鳃鳗性别比分析:JAGS贝叶斯分层逻辑回归MCMC采样模型应用
【视频讲解】R语言海七鳃鳗性别比分析:JAGS贝叶斯分层逻辑回归MCMC采样模型应用



